 Previous Page Next Page
Previous Page Next Page
The following are elements contained in business views.
Organizing data required by a user into multiple categories or multiple levels of categories is meaningful, and makes it easy to use. End users can use categories to find data elements they need to use without knowing the underlying table names although sometimes the table names are used as categories.
Categories have no affect on the way reports get data at runtime. They are simply for the end users to more easily find the data they need.
Custom aggregations are special aggregations used for sophisticated mathematic and logic calculation purposes. They are created using the Formula Editor and are defined based on the elements in a business view and the built-in functions including aggregation functions, mathematic and logic calculation related functions. Custom aggregations can be created as aggregation objects or as dynamic formulas that are used as aggregations in a business view.
When using a custom aggregation in a data component, you need to make sure the group elements referenced in the custom aggregation are also added as table group-by field, crosstab column/row field or chart category/series field in the data component.
The expression for a custom aggregation is defined by relative member set and aggregation. It returns a single value or an array.
The general expression structure of a custom aggregation is @(<Group Collection>, <Aggregation>) or @(<Group Collection>, <Detail>).
The following details each segment in the expression.
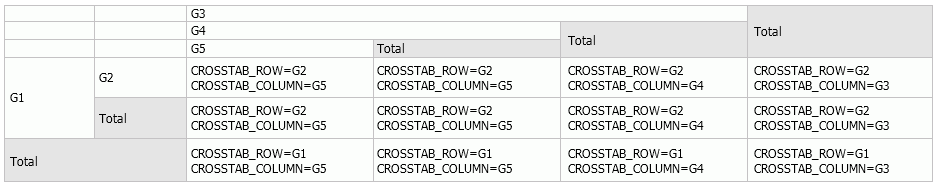
@"Customers.Country".In the following example, G1, G2, G3, G4, and G5 are group names.
@dim means @dim:CURRENT
@dim: means @dim:CURRENT
@dim:"" zero length string, means @dim:CURRENT
@"Orders Detail.Total Quantity".Loop reference is not supported, for example:
Navigation functions used in custom aggregation expressions
When composing the expression of a custom aggregation, you can use a navigation function nextMember() or prevMember() to navigate the next/previous member of a group or detail object. The navigation function can be used as the member argument in the expression of a custom aggregation.
The navigation functions do not actually return a member because formulas do not have a member data type. Instead, the functions only locate a specific member of a group or detail object when a custom aggregation expression is executed on a specific group node or on a crosstab cell. When the custom aggregation is executed on an ALL member, the functions will always locate the ALL member itself.
The order of the members could be the following:
Whether the members of a group or detail object can be located by a navigation function depends on whether the range of members is defined clearly. The range of members of a group or detail object is confined to the current values of all the parent groups if there are any parent groups. The hierarchy of groups is taken into consideration. For example, we have two groups Country and City with members as below:
China
Beijing
Shanghai
USA
New York
When talking about city.FIRSTMEMBER, we first consider what the country is. If current country is China, then it is Beijing and city.LASTMEMBER is Shanghai. If current country is USA, then it is New York. In this way, inappropriate combinations such as the country China and the city New York can be effectively avoided.
Note: Since the combination of the country China and the city New York in a crosstab cell is displayed as blank, the navigation functions will not execute on such combination and therefore the corresponding crosstab cells are kept as blank.
Examples of custom aggregation expressions
@(@"Orders Detail.Sales Year":ALL,@"Customers.Country":"USA",Sum(@"Orders Detail.Quantity"))@(@"MonthOfOrderDate":CURRENT,@"Orders Detail.Total Quantity") - @(@"MonthOfOrderDate":PrevMember(),@"Orders Detail.Total Quantity")@(@"Customers.Country":"USA",@"Orders Detail.Total Quantity") / Sum(@"Orders Detail.Quantity")@"Orders Detail.Total Quantity" / Sum(@"Orders Detail.Quantity")Average(@(@"F_day":Children,@"Count_Order ID")). Here F_day is a dynamic formula used as group which is defined as: ForeachDay(@"Orders Detail.Order Date")@(@Country:"USA",@Year:CHILDREN, @@CTF1). Here CTF1 is the name of a crosstab formula.Custom aggregation calculation logic
The calculation of custom aggregations is based on data components. The following introduces the calculation logic in a crosstab. Calculation on chart category and series is similar to that on crosstab. Other components with group structure can be regarded as one-direction crosstabs.
For exmaple, a custom aggregation is defined as @(@Year:CURRENT, @Month:CURRENT, Sum(@Sales)), which contains the two groups @Year:CURRENT and @Month:CURRENT, when it is used in a crosstab with row header Country and column header Region, Country and Region will also determine member combination, so the expression will be @(@Year:CURRENT, @Month:CURRENT, @Country:CURRENT, @Region:CURRENT, Sum(@Sales)).
If a custom aggregation uses variable as <Group Name> in the expression, such as CURRENT, CROSSTAB_ROW, CROSSTAB_COLUMN, CHART_CATEGORY, and CHART_SERIES, during the calculation the variable need to be replaced by a group name in the data component, and which group name will be used depends on the position where the custom aggregation is inserted in the data component.
In the above example, JReport knows Country and Region member values of the cells, but cannot know that of Year and Month, so Year and Month members are ALL, and the expression will be @(@Year:ALL, @Month:ALL, @Country:"USA", @Region:"CA", Sum(@Sales)).
When the Running functions are used in the custom aggregation expression, if the group member combination does not have relative cell in the crosstab, it returns Null.
During the custom aggregation calculation, error may occur when any of the following happens:
For example: CusAgg1 is defined as @(CURRERT:CURRENT, @Year:"2014", Sum(@Sales)) and is inserted into a data component's Year group. During calculation, <Group Collection> is @Year:CURRENT, @Year:PrevMember(), where group names are duplicated.