 Previous Page Next Page
Previous Page Next Page
Parameter Application Cases
Dynamically filtering queries
Dynamically grouping/sorting report data
Grouping data dynamically
Sorting data dynamically
Filtering a parameter with another parameter
Controlling multiple parameters in a report
Applying RLS to parameters
Supplementing WHERE portions
In JReport, parameters can be used in many situations. The usage of parameters can greatly facilitate your reporting work.
Dynamically filtering queries
You can use a parameter in a WHERE clause so that the query result can vary each time according to the entered parameter value. This is the most common usage of parameters.
The feature works the same for JReport queries created with the Query Editor, business views, datasets, imported SQL files and imported APEs (it is $match stage instead of WHERE clause for APE). When using imported SQL, simply put @Parameter or :Parameter Name directly into the SQL file to be imported; for imported APE, put @Parameter or ?Parameter Name in the JSON file to be imported. JReport will provide the default values when you import the file so the database recognizes the syntax.
The following example shows using a parameter to filter a JReport query dynamically.
- Make sure SampleReports.cat is the currently open catalog file. If not click File > Open Catalog to open it from
<install_root>\Demo\Reports\SampleReports.
- In the Catalog Manager, expand the desired data source and create a type-in parameter named IDSet of Integer type with the default values 1, 10, and 20, and enable the Allow Multiple Values option.
- In the same data source, create a query CustomersInfo on the table Customers. Select all the fields contained in the table.
- In the Query Editor, click Menu > Query > Filter.
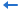
- Filter the records of the query by adding a condition as follows in the Search Condition dialog (for details, see Filtering with the filter format):
- Create a page report with a table in it based on the query as follows: have the fields Customer ID, Customer Name, City and Phone displayed in the table and apply the Commercial style.
- View the report. In the Enter Parameter Values dialog, click
 next to the value field of IDSet.
next to the value field of IDSet.
- In the Enter Values dialog, uncheck the All option, add the listed values 1, 10, and 20 to the right box, and then click OK. You will find that the records with Customer ID equal to 1, 10 and 20 have been retrieved.

- View the report again. This time, in the Enter Values dialog, remove 1, 10, and 20 from the Selected Values box first. Enter the values 3, 7, 9, 11, 15, and 25 in the Enter Values field and add them into the Selected Values box one by one. Then click OK. Now, the records for the specified Customer IDs are displayed.

To view the report with full data, select the All option and then click OK in the Enter Values dialog.
Notes:
- The parameter's data type must be set according to the field type and the manner in which you use the parameter. For example, if the field is a number, define a parameter to be Number type also.
- When specifying the value for a parameter used in a filter condition, if the parameter is of String type:
- When the parameter is used for a JReport query, imported SQL file, business view or dataset:
- If it is used in the format :ParameterName, the parameter value you type should be with single quotation marks, for example, 'USA'.
- If it is used in the format @ParameterName, the parameter value should be without single quotation marks, for example, USA. Once you input a parameter value with single quotation marks, the quotation marks will be recognized as a part of the parameter value.
- When it is used for an imported APE, the parameter value should be with double quotation marks, for example, "USA".
If the parameter is not of String type, you can type the parameter value directly, for example, 1234.
Dynamically grouping/sorting report data
An important usage of parameters is to use them to dynamically group and sort data in a report, which enables the end users to specify the grouping and sorting conditions at runtime.
The Dynamic Group and Dynamic Sort features only apply to tables and banded objects created using query resources in page reports.
Grouping data dynamically
You can make a multi-level group report by selecting a field as grouping criterion for the report. However, because the grouping criteria are definite, if you want to group several times according to different grouping criteria but based on the same query it is cumbersome. For example, you want to make three employee list reports with different grouping criteria, the first one is grouped by their first name, the second one is by the hire date and the third one is by their salary, then you have to repeat the steps of setting query, selecting fields as grouping criteria, and so on, which is not efficient.
For this case you can use the Dynamic Group feature of JReport Designer, which means grouping criteria is a dynamic process. You don't need to repeat the same steps to make multiple reports with different grouping criteria. You can just predefine a parameter using String value type and add it to the group list. Then when you run the report, the parameter dialog prompts the end user to select a field to group by. All the acceptable group-by fields are listed in a drop-down list. You can select any of them as grouping criterion.
You can create a table in a page report as follows to achieve the goal:
- Make sure SampleReports.cat is the currently open catalog file. If not click File > Open Catalog to open it from
<install_root>\Demo\Reports\SampleReports.
- Click File > New > Page Report.
- In the Select Component for Page Report dialog, select the Table (Group Left Above) component type and click OK.
- In the Data screen of the Table Wizard, select the query EmployeeInformation in Data Source 1. Click Next.
- In the Display screen, add the following fields in the selected query to the table: Hire Date, Name, Home Phone and Salary. Click Next.
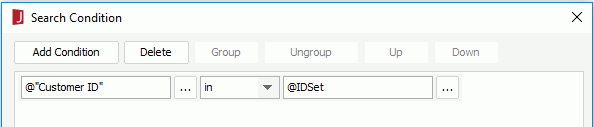
- In the Resources box of the Group screen, click <New Parameter...> in the Parameters node to create a type-in parameter named pGroupBy of String type (leave the other settings to their default).
- Specify to group the report on the just created parameter pGroupBy and use Ascend as the sorting order.
- Click Finish in the Table Wizard to create the table.
- Click the View tab to preview the report. The Enter Parameter Values dialog appears for you to specify the grouping criterion.
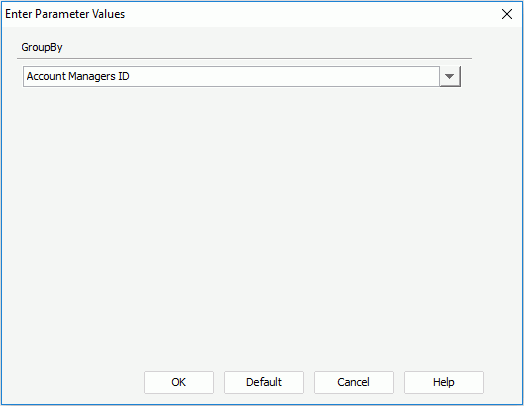
All the DBFields in the query the table uses and the valid formulas for these DBFields are listed in the pGroupBy drop-down list. You can select a field by which to group data in the table.
- Select Employee Position as the parameter value. Data in the table is then grouped by positions of the employees.
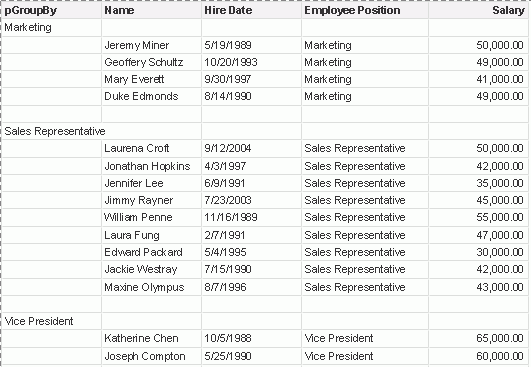
- To group the data by hire date or salary, select Hire Date or Salary from the value drop-down list of pGroupBy.
Sorting data dynamically
The following takes an example to show how to use the Dynamic Sort feature.
- Make sure SampleReports.cat is the currently open catalog file. If not click File > Open Catalog to open it from
<install_root>\Demo\Reports\SampleReports.
- Click File > New > Page Report.
- In the Select Component for Page Report dialog, select the Table (Group Above) component type and click OK.
- In the Data screen of the Table Wizard, select the query EmployeeInformation in Data Source 1. Click Next.
- In the Display screen, add the following fields in the selected query to the table: Hire Date, Name, Home Phone and Salary.
- Click the Sort Fields By button.
- In the Sort Fields By dialog, click <New Parameter...> in the Parameters node in the Resources box to create a type-in parameter named pSortBy of String type (leave the other settings to their default).
- Add the just created parameter pSortBy as the sort-by field.
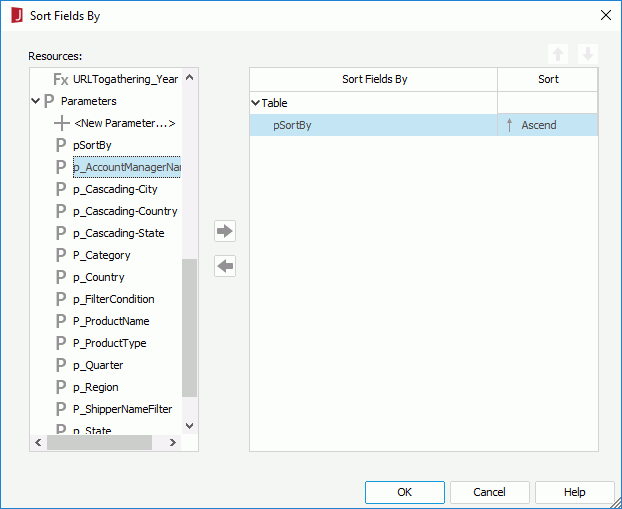
- Select Dynamic Sort from the sort order drop-down list in the Sort column.
- In the Specify Sort Order for dialog, input SortBy Order, then click OK to close the dialog.
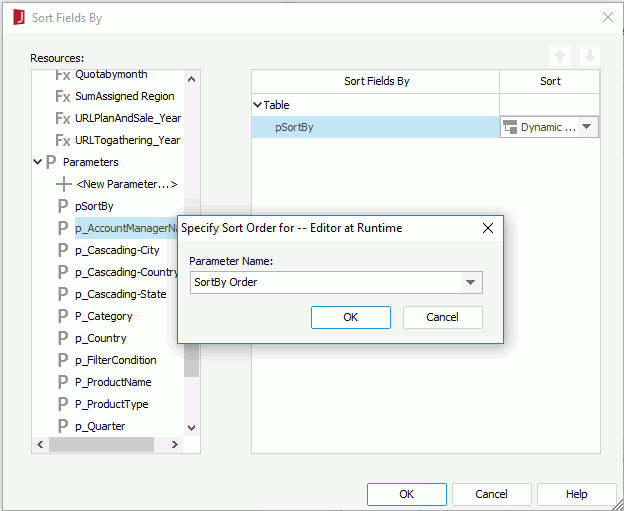
- Click OK in the Sort Fields By dialog to accept the changes.
- Click Finish in the Create Table wizard to create the table.
- Click the View tab to preview the table. The Enter Parameter Values dialog appears for you to specify the sort manner.
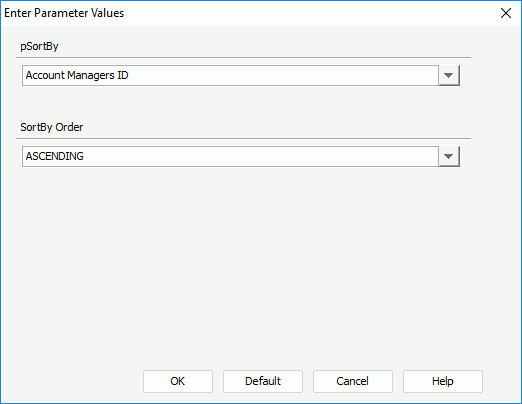
- All the DBFields in the query the table uses and the valid formulas for these DBFields are listed in the pSortBy drop-down list. You can select a field by which to sort the data and then specify the sort order in the SortBy Order drop-down list.
Here, we choose Salary from the pSortBy list and DESCENDING from the SortBy Order list. The records within each group are displayed in descending order according to their salary values.
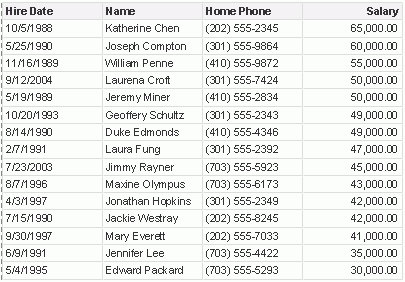
-
Preview the table again and this time select Name from the pSortBy list and ASCENDING from the SortBy Order list. The table displays like this:
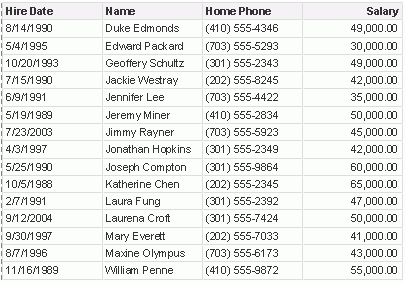
Filtering a parameter with another parameter
You can use the value of one parameter to filter another one. In this way you can create your own cascading parameters such as using pCountry to filter the values returned by a parameter listing available states.
The following examples show you the two methods that you can use to achieve this purpose.
Method 1 (Use this method when the SQL needed to select the parameter values is very simple.)
- Make sure SampleReports.cat is the currently open catalog file. If not click File > Open Catalog to open it from
<install_root>\Demo\Reports\SampleReports.
- In the Catalog Manager, expand the desired data source node.
- Right-click the Parameters node and then click New Parameter. The New Parameter dialog appears.
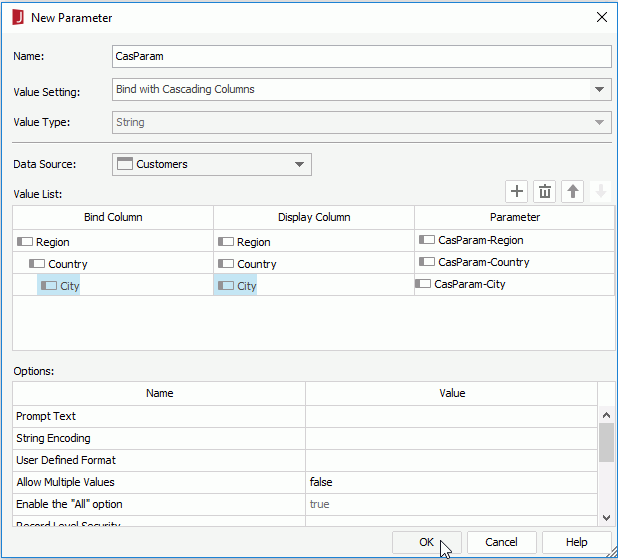
- Enter CasParam in the Name field, select Bind with Cascading Columns from the Value Setting drop-down list, and then select Customers of the Tables type from the Data Source drop-down list.
- Click
 to add a parameter row, select Region as the Bind Column and Display Column, and then click in the Parameter cell to create the parameter in the cascading group.
to add a parameter row, select Region as the Bind Column and Display Column, and then click in the Parameter cell to create the parameter in the cascading group.
- Click
 to add another parameter row, select Country as the Bind Column and Display Column, and then click in the Parameter cell.
to add another parameter row, select Country as the Bind Column and Display Column, and then click in the Parameter cell.
- Click
 to add one more parameter row, select City as the Bind Column and Display Column, click in the Parameter cell, and then click OK in the dialog.
to add one more parameter row, select City as the Bind Column and Display Column, click in the Parameter cell, and then click OK in the dialog.
- In the same data source, create a query CustomersInfo on the table Customers and select all the fields in the table.
- Filter the records of the query by adding a condition as follows in the Search Condition dialog (for details, see Filtering with the filter format):
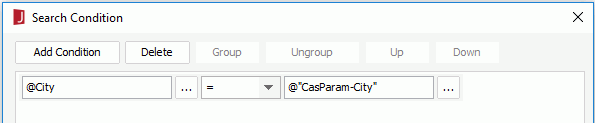
- Create a page report with a table in it based on the query, and have the fields Customer Name, City, Country and Region displayed in the report.
- View the report and the Enter Parameter Values dialog appears.
- From the region drop-down list, select a region, then only the countries in the selected region will be displayed in the country drop-down list. Choose a country from the list, and then only the cities in the selected country will be displayed in the city drop-down list.
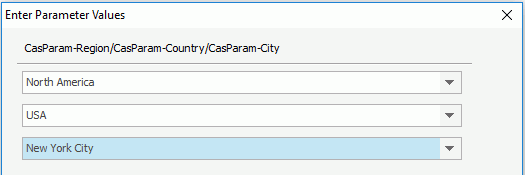
- Click OK. You will now find that only the specified records are shown.
Method 2 (Use this method when you need more customized SQL to show the correct values.)
- Make sure SampleReports.cat is the currently open catalog file. If not click File > Open Catalog to open it from
<install_root>\Demo\Reports\SampleReports.
- In the Catalog Manager, expand the desired data source node.
- Right-click the Parameters node and then click New Parameter.
- Create a parameter named ParamRegion, select Bind with Single Column from the Value Setting drop-down list, select Tables and Views from the Source drop-down list, select Region as the Bind Column and Display Column. Then in the value cell of the Import SQL option, you can see the following statement:
SELECT DISTINCT CUSTOMERS.REGION FROM CUSTOMERS
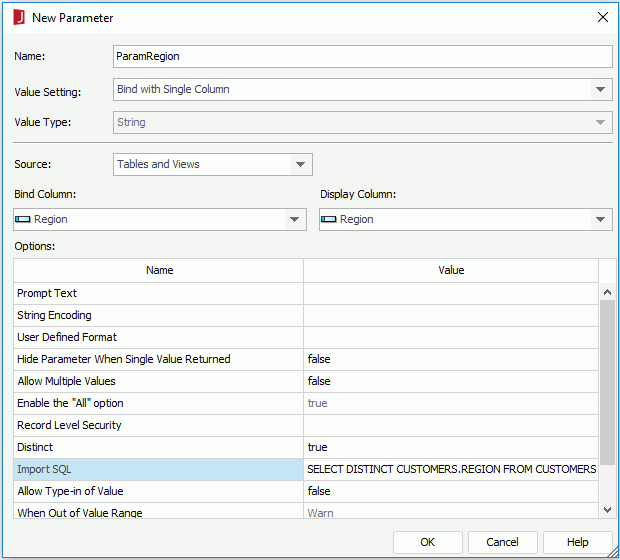
- Create another parameter named ParamCountry. Bind it with the column Country, then click
 in the value cell of Import SQL and edit its SQL statement as follows:
in the value cell of Import SQL and edit its SQL statement as follows:
SELECT DISTINCT CUSTOMERS.COUNTRY FROM CUSTOMERS WHERE (Customers.Region=@ParamRegion and Customers.YTDSALES > 0 )
- Create one more parameter named ParamCity. Bind it with the column City, and then edit its SQL statement as follows:
SELECT DISTINCT CUSTOMERS.City FROM CUSTOMERS WHERE (Customers.Country=@ParamCountry and Customers.YTDSALES > 0 )
- In the same data source, create a query CustomersInfo on the table Customers and select all the fields in the table, and filter the records of the query by adding a condition as follows:
CUSTOMERS.CITY=@ParamCity
- Create a page report with a table in it based on the query, and have the fields Customer Name, City, Country and Region displayed in the report.
- View the report. In the Enter Parameter Values dialog, you can use the value of ParamRegion to filter the value of ParamCounty, and use the value of ParamCounty to filter the value of ParamCity. You will not see any countries and cities where their are no sales.
Controlling multiple parameters in a report
When multiple parameters are used in a report, but you only want to show some of them when running it, you can group them and then select the parameter you want for the report. The parameter values not entered will use their default value. See the example below:
- Make sure SampleReports.cat is the currently open catalog file. If not click File > Open Catalog to open it from
<install_root>\Demo\Reports\SampleReports.
- In the Catalog Manager, expand Data Source 1, then right-click the Parameters node and select New Parameter.
- In the New Parameter dialog, enter GroupParam in the Name field, select Parameters from the Value Type drop-down list, then add three parameters as the default values of GroupParam as shown in the following image:
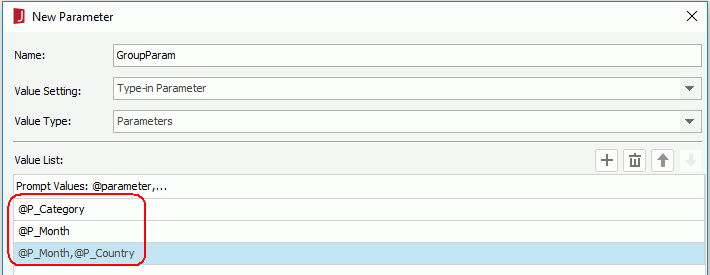
- Open an existing page report. Insert the parameters P_Category, P_Month, P_Country, and GroupParam into a report tab of the report.
- View the report, and the Enter Parameter Values dialog appears. You can select the parameter you want from the GroupParam drop-down list.
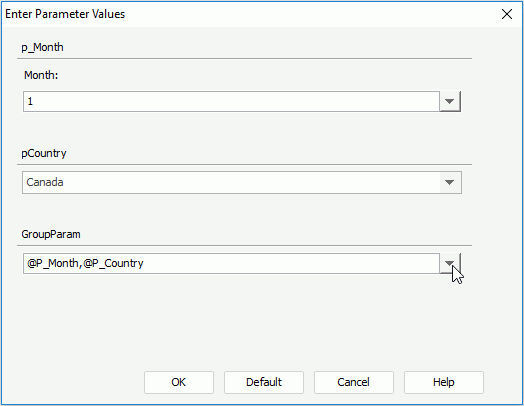
Select @P_Category, the P_Category parameter is displayed in the dialog and you can select or type in a value for the parameter. If you select @P_Month,@P_Country, then both the parameters P_Month and P_Country will be displayed for you to specify values with which to run the report.
Applying RLS to parameters
For parameters bound with DBFields, you can apply record-level security policies (RLS) of data source scope to them. The security policy is specified on the DBField that is bound to the parameter. At runtime, end users will only see parameter values which the security identifier allows to view in the parameter value drop-down list.
The following example explains how to apply RLS to the value drop-down list of a parameter in detail.
- Make sure SampleReports.cat is the currently open catalog file. If not click File > Open Catalog to open it from
<install_root>\Demo\Reports\SampleReports.
- In the Catalog Manager, expand the data source where you want to create the parameter.
- Right-click Security Entry in the Security node, click New Security Entry on the shortcut menu, then name the security policy CusCountry.
- In the Security dialog, make sure Valid RLS is checked at the bottom left.
- Click
 and select Add User. In the Add User dialog, enter John in the User text box and click OK.
and select Add User. In the Add User dialog, enter John in the User text box and click OK.
- In the Record Level Security tab, edit the security condition as below to make John has the permission to view records in Canada only (for details about how to compose a security condition, click here).
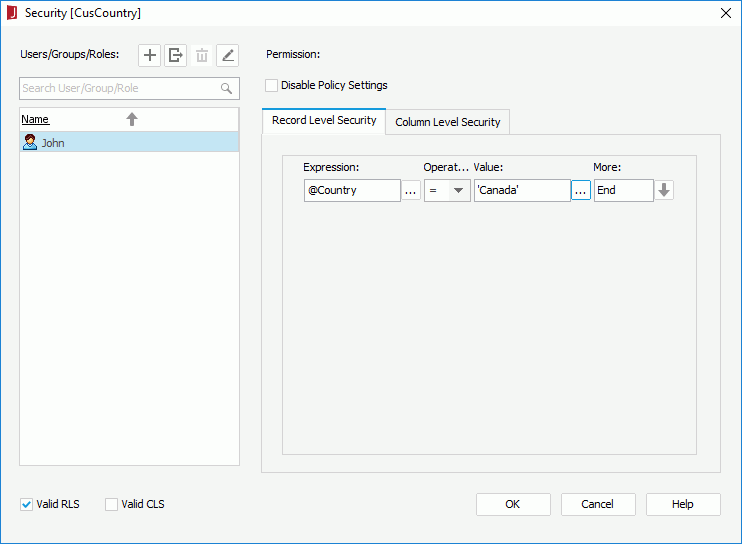
- Add another user David which has the permission to view records in the United Kingdom only.
- Click OK to exit the Security dialog.
- In the same data source, right-click the Parameters node and click New Parameter on the shortcut menu.
- In the New Parameter dialog, enter pCountry in the Name field, select Bind with Single Column from the Value Setting drop-down list, and bind the parameter with the Country column. In the Options box, select CusCountry as value of Record Level Security, and then set the Distinct option to true. Click OK.
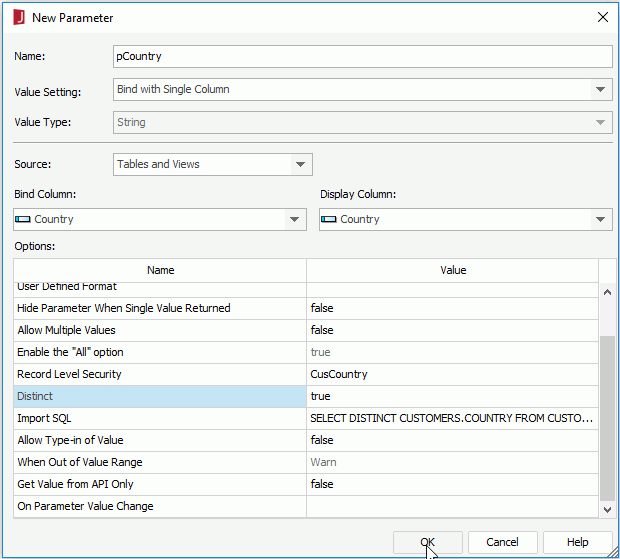
- Create a query CustomersInfo on the table Customers. Select all the fields contained in the table.
- Create a page report with a standard banded object in it based on the query, and have the fields Customer ID, Customer Name, Country and Phone displayed in the report.
- In the Data panel, right-click the node that represents the query, and then select Edit Query from the shortcut menu.
- In the Query Editor, click Menu > Query > Filter.
- In the Search Condition dialog, add a condition for the query as follows (for details, see Filtering with the filter format):
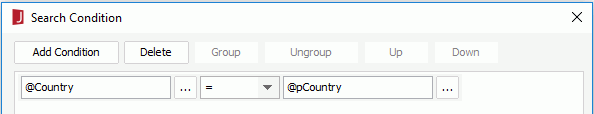
- Click OK to apply the changes to the query.
- Click File > Options, in the General category of the Options dialog, set the User Name as John.
- View the report, and the Enter Parameter Values dialog is displayed.
- Click the parameter value drop-down list, and you can see that only Canada is displayed for the user name.
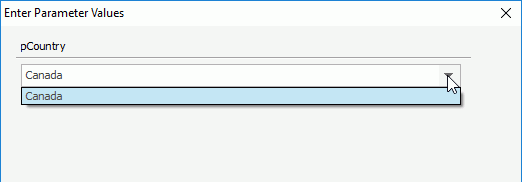
- Set the user name as David in the Options dialog and view the report again. You will find that only the value United Kingdom is displayed in the parameter value drop-down list this time.
Notes:
- When applying an RLS policy to a parameter bound with a column, you must make sure the parameter's bound column and the column used to set conditions in the RLS policy are in the same table. In addition, if the RLS policy also contains conditions defined on other columns, all the columns must be in the same table, and the RLS policy cannot contain parameters and formulas; otherwise, when you apply the RLS to the parameter, the RLS would not work properly.
- When you have applied an RLS policy to a parameter and then you edit the SQL statement of the parameter via the Import SQL option in the parameter dialog, the parameter value drop-down list may be Null because the changed SQL statement may not match the permissions of the RLS.
- When previewing a report that contains parameters applied with RLS in the Page Report Result or Web Report Result format in JReport Designer, you need to make sure your RLS policy contains the user Jinfonet. That is because the user Jinfonet is the default and only user of the preview server. Any other users in the RLS policy cannot be recognized by the preview server.
Supplementing WHERE portions
JReport allows you to change a query at runtime using the API. To do this, you can call the method setWherePortion() from your Java application. However, by calling this method, the original WHERE portion of the query will be replaced. If you want to append the runtime WHERE portion to the original one instead of replacing it/them, you can do it in the following way without using the Java API:
- Make sure SampleReports.cat is the currently open catalog file. If not click File > Open Catalog to open it from
<install_root>\Demo\Reports\SampleReports.
- In the Catalog Manager, expand the desired data source and create a type-in parameter named p_Portion of String type (leave the other settings to their default).
- In the same data source, create a query CustomersInfo on the table Customers. Select all the fields contained in the table.
- Create a page report with a table in it based on the query, and have the fields Customer ID, Customer Name, City and Phone displayed in the report, then apply the Commercial style.
- In the Data panel, right-click the node that represents the query, and then select Edit Query from the shortcut menu.
- In the Query Editor, click Menu > Query > Filter.
- In the Search Condition dialog, add two condition lines (WHERE portions) for the query as follows (for details, see Filtering with the filter format):
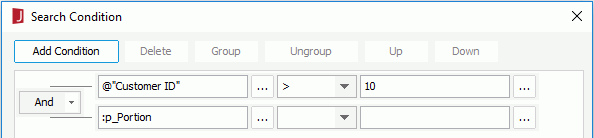
The colon is used to append the parameter value (of String type) to the first condition line instead of replacing it.
- Click OK to apply the change to the query.
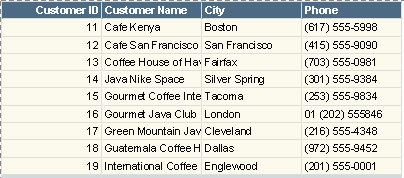
- View the report, and in the Enter Parameter Values dialog, write a WHERE portion in standard SQL syntax as value of p_Portion, for example, CUSTOMERID<20. Then, both of the two WHERE portions will be used to filter the query.
 Previous Page Next Page
Previous Page Next Page
 Previous Page Next Page
Previous Page Next Page

 next to the value field of IDSet.
next to the value field of IDSet.









 to add a parameter row, select Region as the Bind Column and Display Column, and then click in the Parameter cell to create the parameter in the cascading group.
to add a parameter row, select Region as the Bind Column and Display Column, and then click in the Parameter cell to create the parameter in the cascading group. to add another parameter row, select Country as the Bind Column and Display Column, and then click in the Parameter cell.
to add another parameter row, select Country as the Bind Column and Display Column, and then click in the Parameter cell. to add one more parameter row, select City as the Bind Column and Display Column, click in the Parameter cell, and then click OK in the dialog.
to add one more parameter row, select City as the Bind Column and Display Column, click in the Parameter cell, and then click OK in the dialog.




 in the value cell of Import SQL and edit its SQL statement as follows:
in the value cell of Import SQL and edit its SQL statement as follows:


 and select Add User. In the Add User dialog, enter John in the User text box and click OK.
and select Add User. In the Add User dialog, enter John in the User text box and click OK.




