 Previous Page Next Page
Previous Page Next Page
Creating the aggregation pipeline expressions
For users who wish to write their own MongoDB aggregation pipeline expressions (APE), JReport allows them to put the expressions into JSON files (.json) and import the files into a catalog via the specified MongoDB connection. JReport can then load data from the MongoDB database by the aggregation pipeline expressions in the imported JSON files.
At present each JSON file can contain only one aggregation pipeline expression. For details about the expression definition, refer to https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/core/aggregation-pipeline/.
The imported JSON files can work similarly as imported SQL files, for example, you can use imported APEs to build queries and business views, and create page reports directly.
When you write aggregation pipeline expressions, you need to make sure they follow JSON format. The key and value pairs in an aggregation pipeline expression should be marked with double quotation marks (double quotation marks are not needed for a value whose data type is not String), and enclosed in a pair of square brackets. Moreover, when the data in the MongoDB database is of hierarchical structure, in order to get all detail data in the MongoDB databases, it is suggested that you add $unwind in the expression, then a tabular with all data records can be returned; otherwise a hierarchical structure with partial data records will be returned.
The following is an example:
[ {"$match" : { "CUSTOMERID" : { "$gt" : 10}}}, { "$project" : { "CUSTOMERNAME" : 1 , "COUNTRY" : 1 , "CUSTOMERID" : 1}}, { "$sort" : { "COUNTRY" : 1}} ]
In an aggregation pipeline expression, you can use parameters and constant level formulas predefined in the catalog data source in which the MongoDB connection is created in the format @FieldName or ?FieldName to calculate your data. For example, if you need to get different result sets at runtime, you can reference parameters in the $match stage of the expression to dynamically filter the data. In the above example, if you want to use a parameter to return a result set in which the customer ID is greater than the parameter, then the $match stage would be like this:
{"$match" : { "CUSTOMERID" : { "$gt" : @pID}}}
Where, pID is a parameter and fID is a constant level formula created in the catalog.
Besides using parameters, you can also use the special field User Name as @username in the $match stage of the aggregation pipeline expressions to filter data dynamically.
Note: When the Scope of All Values property of a parameter is set to All Values in Database, the parameter cannot be used in aggregation pipeline expressions.
After you have set up the MongoDB connection and saved aggregation pipeline expressions in JSON files, you can import them into the JReport catalog as follows:
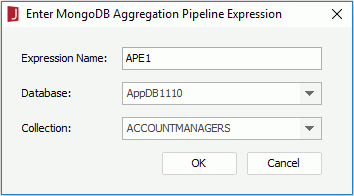
The JSON file is then added in the Imported APEs node in the catalog resource tree. You can right-click it and select Show APE from the shortcut menu to view the aggregation pipeline expression in the JSON file if you want. The format of the JSON file, such as comments, are maintained when it is added into the JReport catalog.
When you import a JSON file via the Data screen of the report wizard, you should also specify the MongoDB connection based on which to execute the aggregation pipeline expression in the selected JSON file from the Connection drop-down list.
If you make any change to the aggregation pipeline expression in an JSON file, you need to update the JSON file in the JReport catalog so that reports built based on the aggregation pipeline expression can work properly.