 Previous Page Next Page
Previous Page Next Page
Using Data Sources via OOJDBC
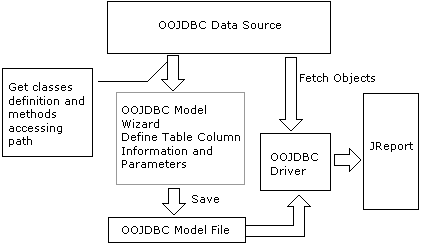
Main frame for OOJDBC in JReport
Using XML file as data source via OOJDBC
Example 1: Importing the XML file indirectly
Example 2: Importing the XML file directly
Example 3: XML file with dynamic parameters
Using class file as data source via OOJDBC
Using CSV file as data source via OOJDBC
OOJDBC (Object Oriented Java Database Connection) is defined to cover an OODS (Object Oriented Data Source) with a JDBC interface. It is similar to a JDBC driver and is based on a Java application, EJB (Enterprise Java Bean), LDAP (Light Weight Directory Access Protocol), which can be defined as a database. JReport provides a tool named Model Wizard, which you can run to import data via an OOJDBC data source.
Main frame for OOJDBC in JReport
OOJDBC in JReport includes Model Wizard and OOJDBC Driver.
- Model Wizard
Open/Save model file
Define a Java class as a table
Define a method as a column
How to access the instance of the class
- OOJDBC Driver
Read the table/column definitions from model file
Return meta-data to JReport
Construct QUERY data
Return record to JReport
Using XML file as data source via OOJDBC
JReport Designer supports accessing XML data sources via OOJDBC. JReport also supports using XML directly which is recommended over using OOJDBC (see XML Connections).
Example 1: Importing the XML file indirectly
In this example, employee.xml in <install_root>\help\samples\OOJDBC will be used. Store it to <install_root>\Demo\Reports\TutorialReports first. Then follow the steps below to import the file to a catalog.
Task 1: Importing the XML file using the Model Wizard
- Run ModelWizard.bat in
<install_root>\bin to open the Object Source Wizard.
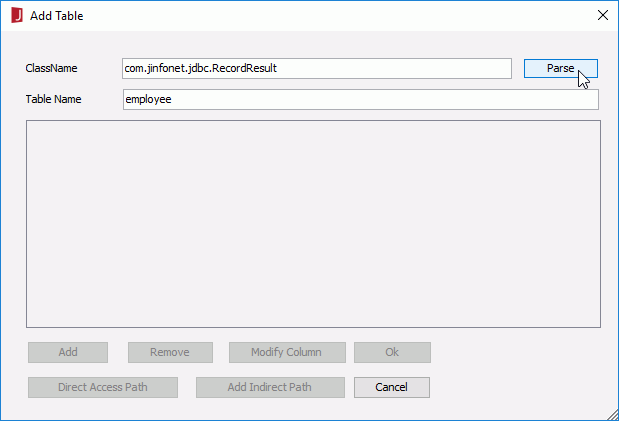
- Click File > Add Table.
- In the Add Table dialog, specify the class and table name as required. Here, we fill in the Table Name as employee and ClassName as com.jinfonet.jdbc.RecordResult (a class of Jinfonet). Then click the Parse button.
Below are explantions about the options in the dialog:
| Options |
Description |
| Column Name |
Methods of the class you have defined. |
| SQL Type |
Returned type of your column name. You can double-click the field and choose the SQL type you want. |
| Precision |
Precision of the current column. You can click on the field and change it manually. |
| Scale |
Scale of the current column. You can also click on the field and change it manually. |
| Nullable |
Current status of the column (null or not). You can double-click on the field and choose the current status: Nullable, No Nulls or Nullable Unknown. |
| Currency |
If your DBField contains $, you should check it. |
| Add |
Adds new columns. |
| Remove |
Removes the selected column. |
| Modify Column |
Modifies parameters of the current table. |
| OK |
Adds the table. |
| Direct Access Path |
Specifies the path for the table. OOJDBC driver can save and restore the table you have defined through
this path. |
| Cancel |
Cancels the operation and closes the Add Table dialog. |
- Click the Remove button to get rid of all the existing columns in the Add Table dialog, and then click the Add button to add a new column.
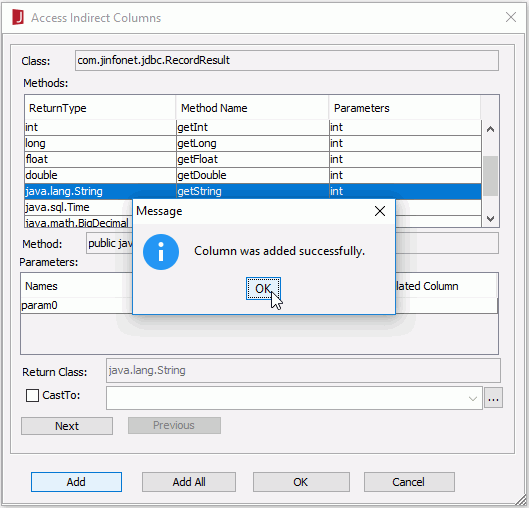
- In the Access Indirect Columns dialog, specify the data type of the column.
In this example, we will add a column of String type, so click java.lang.String in the ReturnType column of the Methods box, then click the Add button. Click OK to return to the Add Table dialog.
- In the Add Table dialog, click Direct Access Path to define the accessing path of the table in the Access Method dialog.
- Fill in com.jinfonet.jdbc.xml.XMLReader in the Root Class Name text box, click the Parse button and check Show Static Methods Only.
- Click the shown method. In the Parameters box, fill in the default values for param0 and param1 as required. For example, for param0, fill in
file:///C:/JReport/Designer/Demo/Reports/TutorialReports/employee.xml, then for param1, fill in record employee root employee column first_name 12 path document.employee.first_name.
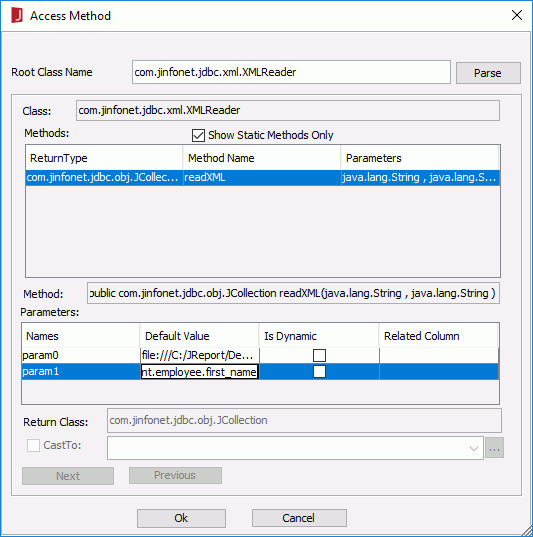
The following are explanations about the parameters.
- param0 is the valid XML file name with its path.
- param1 is the query sentence for selecting the column to be used for reporting from the XML file. record is the keyword, followed with the XML file name (without the extension .xml). Following this is another keyword column with the actual tag name from the XML file.
Below is the part quoted from employee.xml:
<employee>
<id>0799</id>
<first_name>Jack</first_name>
<second_name>Smith</second_name>
<birthday>12/28/75</birthday>
<title>manager</title>
<salary>$7000.00</salary>
</employee>
|
Since first_name is required, you should then give the actual tag name here. The number afterwards is the SQL type of the column. "12" is for String type. For detailed information about Java SQL types, refer to JDK package java.sql.types.java.
Notes:
- In param1, the order of the columns is dependent on the default values given when adding the column.
- The SQL type BINARY, VARBINARY and LONGVARBINARY are not supported.
- Click OK to return to the Add Table dialog.
- Now you can see that the column has been added in the Add Table dialog. You can rename the default column name by editing in the Column Name column. You are recommended to give the name as the actual tag definition in the .xml file, for example first_name.
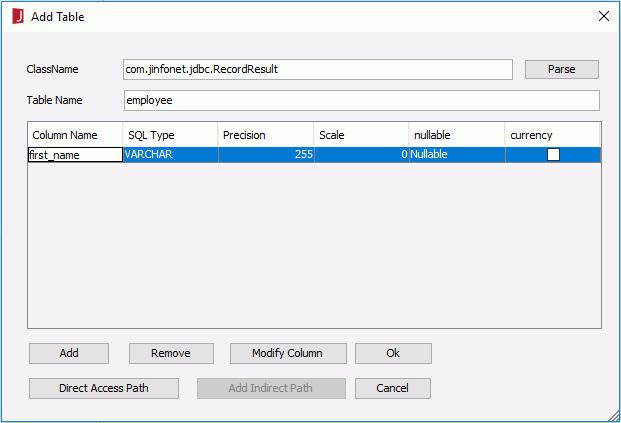
- Click the OK button, and the table employee will now have been added to the Object Source Wizard.
- Click File > Save in the wizard. You will then be prompted to save the ODF file. You should save it to
<install_root>\lib or the directory where the catalog will be. Here we save it as employee.odf.
Notes:
- If you use dynamic parameters, that is you check the Is Dynamic option, the syntax of the method is an array of Boolean values which indicates which parameter is dynamic at runtime. If the parameter is dynamic the value should be prompted and initialized before executing an SQL. In addition, when you choose the option Is Dynamic, this parameter will be passed to JReport Designer. After you create a connection in the Catalog Manager, you will find it in the Parameters node.
- The same ODF file cannot exist in both
<install_root>\lib and the directory where the catalog is located.
- If you have purchased the readable key, you can also save the ODF file (oojdbc data definition file) to XML format (with extension .odf.xml). For files which have already been saved with an .xml extension, in order to make them available, you can manually change the extension from .xml to .odf.xml.
Task 2: Importing the ODF file into a catalog
- Start JReport Designer.
- Click File > New Catalog.
- In the New Catalog dialog, specify the catalog name, the data source name and the path. The catalog should be located in the directory where you saved the ODF file. For example, if you saved the ODF file in
C:\odf, the new catalog should be created also in C:\odf.
- In the Catalog Manager, right-click the node of a data source and select New JDBC Connection from the shortcut menu. Click JDBC in the Select Connection Type dialog.
- In the Get JDBC Connection Information dialog, enter com.jinfonet.jdbc.obj.ObjectDriver in the Driver text box, type jdbc:jinfonet:object:@Filename in the URL text box. @Filename should be the ODF file name. In the example, it is jdbc:jinfonet:object:@employee.
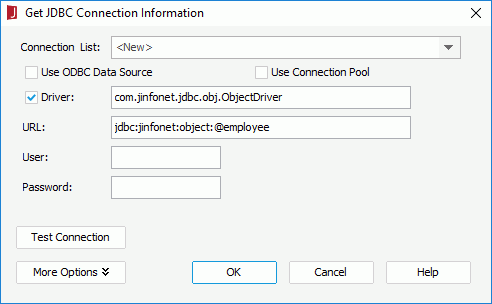
- Click OK to set up the connection.
- In the Add Tables/SQL dialog, click Add Tables (if the dialog is not displayed, click Resume on the Catalog Manager toolbar).
- In the Add Tables/Views/Synonyms dialog, select the table employee and click Add.
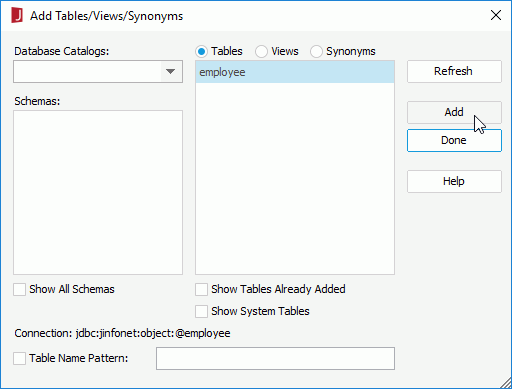
- Click Done to close the Add Tables dialog.
Now, the table employee will have been added into the catalog. You can use it to develop reports as required.
Note: When you publish the catalog and its reports to JReport Server, whether the ODF file is located in <install_root>\lib or in the directory where the catalog is located, it will be deployed to the path where the catalog is located in the server side.
Example 2: Importing the XML file directly
The process of importing an XML file with Model Wizard (as explained in Example 1) can be simplified with JReport's built-in XML file import functionality, and is very easy to use.
In this example, orgchart_data.xml in <install_root>\help\samples\OOJDBC will be used. Store it to <install_root>\Demo\Reports\TutorialReports first. Then follow the steps below to import the file to a catalog.
Task 1: Importing the XML file directly using the Model Wizard
- Run ModelWizard.bat in
<install_root>\bin to open the Object Source Wizard.
- Select File > Import XML Files to bring up the Import XML dialog.
- Click Open to browse to the file orgchart_data.xml.
- Check Column for all elements and change their format and type if necessary.
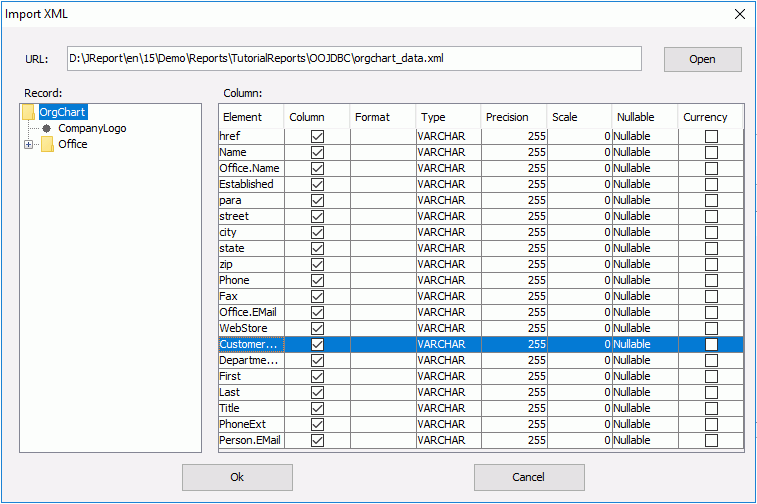
When using certain SQL types, you should input a standard format. There are some examples:
- If the time format is like Tue Aug 27 16:04:00 BST 2002, you should select:
Type: TimeStamp
Format: EEE MMM dd hh:mxm:ss zzz yyyy
- If the time format is like 2002-11-22 11:09:08, you should select:
Type: TimeStamp
Format: yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss
- If the time format is like 11/18/2002 08:20:00, you should select
Type: TimeStamp
Format: M/d/yyyy hh:mm:ss
- If the time format is like 1999-12-05, you should select:
Type: date
Format: yyyy-MM-dd
- If the time format is like 08:20:00, you should select:
Type: time
Format: hh:mm:ss
- If the number is like 50,600, you should select:
Type: integer
Format: ###,###
- If the currency is like $50,600, you should select:
Type: integer
Format: $###,###
- Click OK and the table OrgChart will now have been added to the Object Source Wizard.
- Click File > Save in the wizard. You will then be prompted to save the ODF file. You should save it to
<install_root>\lib or to the directory where the catalog will be located. Here, we save it as orgchart.odf.
Note: The same ODF file cannot exist in both <install_root>\lib and the directory where the catalog will be located.
Task 2: Importing the ODF file into a catalog
- Start JReport Designer.
- Click File > New Catalog.
- In the New Catalog dialog, specify the catalog name, the data source name and the path. The catalog should be located in the directory where you saved the ODF file. For example, if you saved the ODF file in
C:\odf, the new catalog should be created also in C:\odf.
- In the Catalog Manager, right-click the data source node and select New JDBC Connection from the shortcut menu. Click JDBC in the Select Connection Type dialog.
- In the Get JDBC Connection Information dialog, enter com.jinfonet.jdbc.obj.ObjectDriver in the Driver text box, type jdbc:jinfonet:object:@Filename in the URL text box. @Filename should be the ODF file name. In the example, it is jdbc:jinfonet:object:@orgchart.
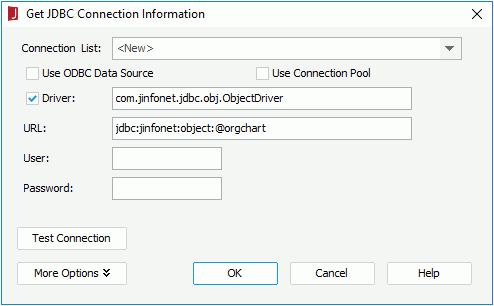
-
Click OK to set up the connection.
- In the Add Tables/SQL dialog, click Add Tables (if the dialog is not displayed, click Resume on the Catalog Manager toolbar).
- In the Add Tables/Views/Synonyms dialog, select the table OrgChart and click Add.
- Click Done to close the Add Tables dialog.
Now, the table OrgChart will be added into the catalog. You can use it to develop reports as required.
Note: When you publish the catalog and its reports to JReport Server, whether the ODF file is located in <install_root>\lib or in the directory where the catalog is located, it will be deployed to the path where the catalog is located on the server side.
Example 3: XML file with dynamic parameters
When you design a report from the tables imported through OOJDBC, and the tables have the same input parameters, but you don't want to input the same parameters again, JReport provides a way to allow you to bind parameters in a catalog, so they can share the same parameter value.
This example demonstrates how to import tables with dynamic parameters from the ODF file generated by the Model Wizard.
Task 1: Importing the XML file using the Model Wizard
- Run ModelWizard.bat in
<install_root>\bin to open the Object Source Wizard.
- Add two tables as shown in Example 1. The first table named employee1 has one String type column, and the second table named employee2 has one Int type column. They have the same input parameter for param0. The default value is
h:\xml\employee.xml. Make sure to check the option Is Dynamic.
- In the Object Source Wizard, click File > Save. You will then be prompted to save the ODF file. You should save it to
<install_root>\lib or the directory where the catalog will be. Here we save it as xmlparam.odf.
Notes:
- If you choose the option Is Dynamic, this parameter will be passed to JReport Designer. After you create a new connection, you will find this parameter in the node Parameters in the Catalog Manager.
- The same ODF file cannot exist in
both <install_root>\lib and the directory where the catalog is to be located.
Task 2: Importing the ODF file into a catalog
- Start JReport Designer.
- Click File > New Catalog.
- In the New Catalog dialog, specify the catalog name, the data source name and the path. The catalog should be located in the directory where you saved the ODF file. For example, if you saved the ODF file in
C:\odf, the new catalog should be created also in C:\odf.
- In the Catalog Manager, create a parameter in an existing catalog data source that is of String data type and is named path. This parameter will be bound to the parameters in the tables that were imported through OOJDBC.
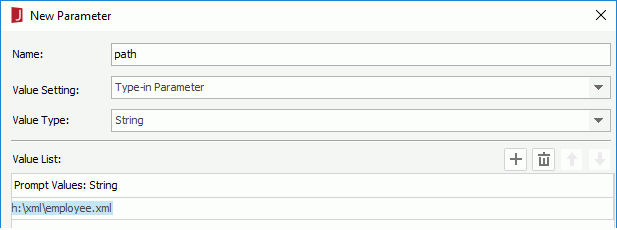
- Right-click the node of the same catalog data source and select New JDBC Connection from the shortcut menu. Click JDBC in the Select Connection Type dialog.
- In the Get JDBC Connection Information dialog, enter com.jinfonet.jdbc.obj.ObjectDriver in the Driver text box, type jdbc:jinfonet:object:@Filename in the URL text box. @Filename should be the ODF file name. In the example, it is jdbc:jinfonet:object:@xmlparam.
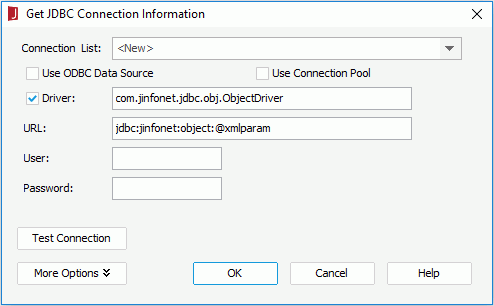
- Click OK to set up the connection.
- In the Add Tables/SQL dialog, click Add Tables (if the dialog is not displayed, click Resume on the Catalog Manager toolbar).
- The Add Tables/Views/Synonyms dialog appears prompting you to add the listed tables. Select the table employee1 and click the Add button. The Dynamic Parameter used in oojdbc tables dialog will then be displayed. Uncheck the checkbox in the New column and select the parameter path from the drop-down list to bind param0 to the parameter path.
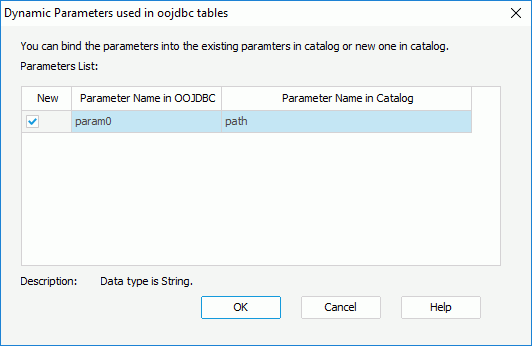
- Repeat the above step to add the employee2 table and bind its parameter param0 to the parameter path. Now the parameters in the two tables will share the same parameter.
- Create a page report on the newly inserted tables.
- When viewing the report, the Enter Parameter Values dialog will be displayed, asking you to input the parameter. You will only need to input the path of imported XML file once since the parameter is shared with the parameters in the two tables.
Tip: You can modify the links between the parameters in OOJDBC and parameters in the JReport catalog.
- In the Catalog Manager, select the table with the dynamic parameters that are to be modified.
- Right-click on the selected table, and select Parameters from the shortcut menu.
- Highlight the parameter in the catalog, and then select the parameter from the drop-down list to bind it to the parameter in OOJDBC.
Using class file as data source via OOJDBC
This document shows an example about how to generate the ODF file in a different way using the file demo.zip in <install_root>\help\samples\OOJDBC, which contains all the necessary classes and methods needed for making the OOJDBC data source work with Java objects.
Preparations
Before the OOJDBC data source works with Java objects, you should do the preparations:
- You should define a class that specifies the column name and the method of getting data from this column. In this example, the class Products.java in demo.zip takes this role. This class file contains the method public int getProductID(), which implies that the column name is ProductID and you can get the product ID via this method.
- You should publish a method to access a group of products. That means OOJDBC needs a result set with multiple rows, and each row is one of the products, so that you should define a class that can retrieve the rows. In this example, the file SQLReader.java in demo.zip takes this role. In this file, there is a static* method JCollection execSQL(String jdbcDriver, String url, String sql), and this method returns a collection that contains the rows of the products. This collection class is com.jinfonet.jdbc.obj.JCollection.
Also, the batch files used to start the Model Wizard, JReport Designer and JReport Server should be modified before you can import the product table and use it to generate reports. To do this:
- Save demo.zip in
<install_root>\help.
- Add it to the class path of the batch file setenv.bat in
<install_root>\bin of both Designer and Server. setenv.bat updates the class path for both the Model Wizard and JReport Designer.
Task 1 : Importing the class file using the Model Wizard
- Run ModelWizard.bat in
<install_root>\bin to open the Object Source Wizard.
- Click Add Table and the Add Table dialog will be displayed.
- In the ClassName field, type com.jinfonet.jdbc.demo.Products, input demo in the Table Name field, and then click the Parse button.
- Click Direct Access Path. In the Access Method dialog, input com.jinfonet.jdbc.demo.SQLReader in the Root Class Name field. Then click the Parse button. In the Methods box, select the method execSQL, and in the Parameters box, fill in the default values as follows:
Param0 (the driver of the database): org.hsqldb.jdbcDriver
Param1 (the connection URL of the database): jdbc:hsqldb:c:\JReport\Designer\Demo\db\JRDemo
Param2 (the user name): sa
Param3 (the password): (no value)
Param4 (the SQL statement): select * from products
- Press the OK button and the table demo will now have been added to the Object Source Wizard.
- Click File > Save in the wizard. You will then be prompted to save the ODF file. You should save it to
<install_root>\lib or the directory where the catalog will be. Here we save it as demo.odf.
Note: The same ODF file cannot exist in both <install_root>\lib and the directory where the catalog is located.
Task 2 : Importing the ODF file into a catalog
- Start JReport Designer.
- Click File > New Catalog.
- In the Catalog Name dialog, specify the catalog name, the data source name and the path. The catalog should be located in the directory where you saved the ODF file. For example, if you saved the ODF file in
C:\odf, the new catalog should be created also in C:\odf.
- In the Catalog Manager, right-click the node of a data source and select New JDBC Connection from the shortcut menu. Click JDBC in the Select Connection Type dialog.
- In the Get JDBC Connection Information dialog, enter com.jinfonet.jdbc.obj.ObjectDriver in the Driver text box, type jdbc:jinfonet:object:@Filename in the URL text box. @Filename should be the .odf name you have saved but do not include the extension. So in the example, it should be jdbc:jinfonet:object:@demo.
- Click OK to set up the connection.
- In the Add Tables/SQL dialog, click Add Tables (if the dialog is not displayed, click Resume on the Catalog Manager toolbar).
- In the Add Tables/Views/Synonyms dialog, select the table demo and click Add.
- Click Done to close the Add Tables dialog.
Now, the table demo has been added into the catalog. You can use it to develop reports as required.
Note: When you publish the catalog and its reports to JReport Server, whether the ODF file is located in <install_root>\lib or in the directory where the catalog is located, it will be published to the path where the catalog is located on the server side.
Tip: JReport provides an interface com.jinfonet.interfaces.query.TableFilter and a simple implementation com.jinfonet.jdbc.obj.TableFilterImpl, which can be used in this example to improve the performance of the select and WHERE clauses in a query. You can extend TableFilterImpl to create your own Reader class. In addition, a demo FilterSQLReader.java in the file demo.zip has been made for your reference. However if you are using FilterSQLReader.java instead of SQLReader.java, you should input com.jinfonet.jdbc.demo.FilterSQLReader in the Root Class Name field of the Access Method dialog.
Using CSV file as data source via OOJDBC
JReport Designer supports CSV as data sources which can be accessed via OOJDBC. You can use this method to import Excel files by using Excel to save the report as .csv.
The following example demonstrates how to import a CSV file to an ODF file generated by the Model Wizard. In this example, employee.csv in <install_root>\help\samples\OOJDBC will be used. Store it to <install_root>\Demo\Reports\TutorialReports first. Then follow the steps below to import the file to a catalog.
Task 1: Importing the CSV file directly using the Model Wizard
- Run ModelWizard.bat in
<install_root>\bin to open the Object Source Wizard.
- Select File > Import Text Files to bring up the Open Text Files dialog.
- Browse to the file employee.csv and then check the First Line Is Column Name checkbox.
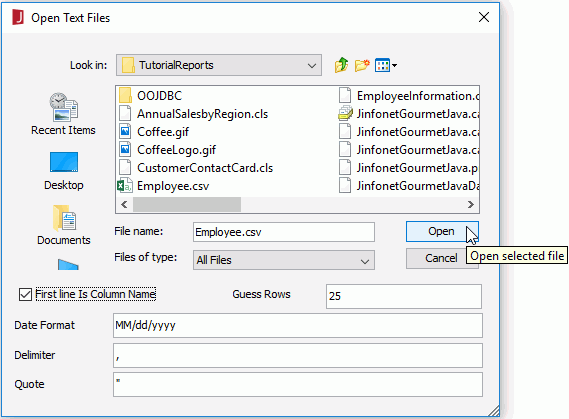
- Click Open and the table Employee will now have been added to the Object Source Wizard.
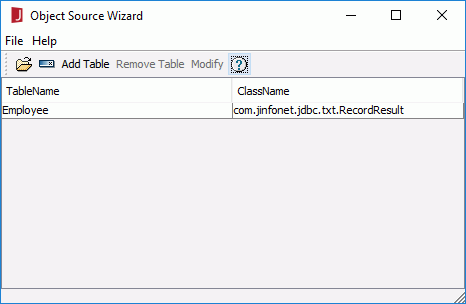
- Click File > Save in the wizard. You will then be prompted to save the ODF file. You should save it to
<install_root>\lib or to the directory where the catalog will be located. Here, we save it as employee_csv.odf.
Note: The same ODF file cannot exist in both <install_root>\lib and the directory where the catalog will be located.
Task 2: Importing the ODF file into a catalog
- Start JReport Designer.
- Click File > New Catalog.
- In the New Catalog dialog, specify the catalog name, the data source name and the path. The catalog should be located in the directory where you saved the ODF file. For example, if you saved the ODF file in
C:\odf, the new catalog should be created also in C:\odf.
- In the Catalog Manager, right-click the node of a data source and select New JDBC Connection from the shortcut menu. Click JDBC in the Select Connection Type dialog.
- In the Get JDBC Connection Information dialog, enter com.jinfonet.jdbc.obj.ObjectDriver in the Driver text box, type jdbc:jinfonet:object:@Filename in the URL text box. @Filename should be the ODF file name. In the example, it is jdbc:jinfonet:object:@employee_csv.
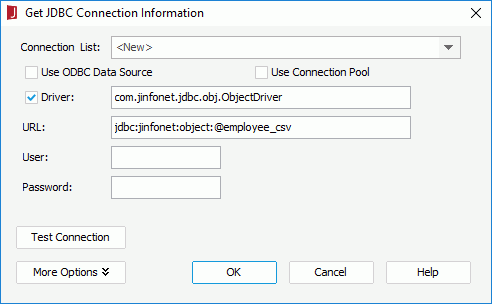
- Click OK to set up the connection.
- In the Add Tables/SQL dialog, click Add Tables (if the dialog is not displayed, click Resume on the Catalog Manager toolbar).
- In the Add Tables/Views/Synonyms dialog, select the table Employee and click Add.
- Click Done to close the Add Tables dialog.
Now, the table Employee will be added into the catalog. You can use it to create query or business view and then develop reports as required.
Note: When you publish the catalog and its reports to JReport Server, whether the ODF file is located in <install_root>\lib or in the directory where the catalog is located, it will be published to the path where the catalog is located on the server side.
 Previous Page Next Page
Previous Page Next Page
 Previous Page Next Page
Previous Page Next Page














